¶ FlexVertex SQL Guide
This document provides a comprehensive guide and reference for the SQL syntax used in our API code examples. It is structured to help users understand and utilize various SQL commands and their applications.
¶ Table of Contents
- FlexVertex SQL Guide
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- When Not to Use SQL
- Ideal Use Cases for SQL
- About the examples
- Basic queries
- Sorting and grouping
- Filtering
- Creating data
- Modifying data
- Removing data
¶ Introduction
Many next-generation information management platforms force developers to learn cryptic languages to work with their data. Not only is this time-consuming, there’s also a real risk that important techniques might get missed, and thus lead to a less than optimal experience.
We felt it would be better to let people use familiar techniques to find and manipulate their data. That’s why we chose to provide a robust SQL implementation that not only lets you search for data, but also interact with it.
Rather than just being a bolt-on afterthought, SQL is integral to everything in FlexVertex. For example, SQL seamlessly works with our groundbreaking Voyager multiverse navigation language. However, even though we offer a powerful SQL option, you’re always free to use our APIs instead, or in combination with it.
FlexVertex SQL provides full create, read, update, and delete capabilities on both standard and embedded objects, all supervised by our fine-grained authorization system. You can choose from our rich function library to streamline interactions with your data, as well as manage result sets. Named parameters, Boolean conditions, list filtering, and arrays are just a few examples of the productivity tools that you can take advantage of when writing your SQL.
Note that in the examples we provide in this guide, all SQL keywords are in UPPERCASE. However, FlexVertex SQL is not case sensitive, so feel free to use whatever case you like. Don't forget, though, that classes and properties are case sensitive.
¶ When Not to Use SQL
While SQL IN FlexVertex is powerful, it has its limitations and is not suitable for certain tasks:
- Data Definition (DDL) tasks: Defining new classes should be handled by Voyager OR other FlexVertex APIs.
- Data Manipulation (DML) tasks: Establishing connections between objects should also be conducted outside of SQL.
- Complex relational operations: Including identifying intricate relationships through joins, are typically managed using Voyager, which is better suited for these tasks due to its specialized capabilities.
¶ Ideal Use Cases for SQL
SQL is particularly useful for:
- Interactive queries and modifications: It provides a user-friendly way to interact with data.
- Navigating the FlexVertex Data Multiverse: It serves as a starting point for data exploration, enabling users to traverse and discover relationships and dependencies across data sets.
¶ About the examples
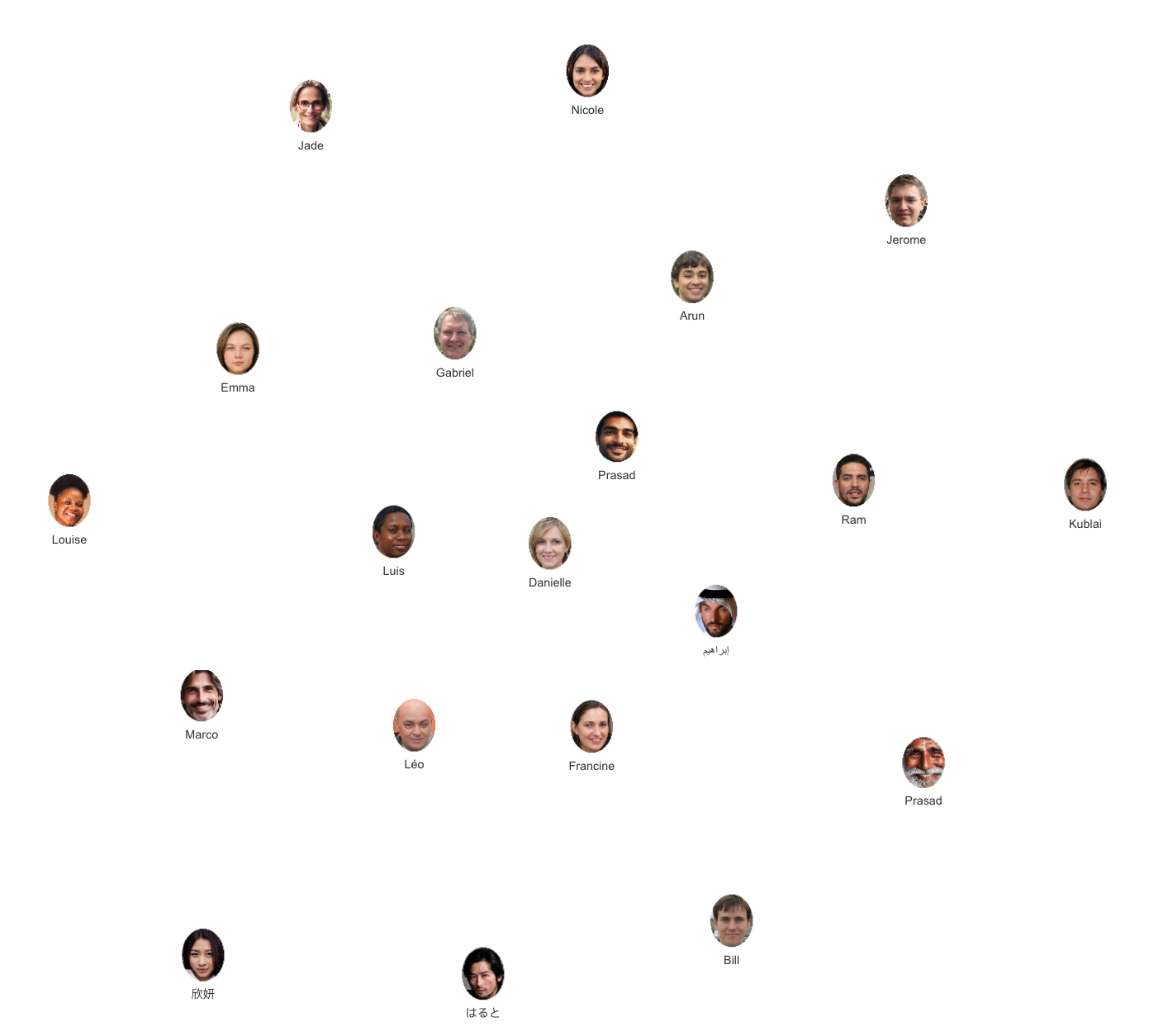
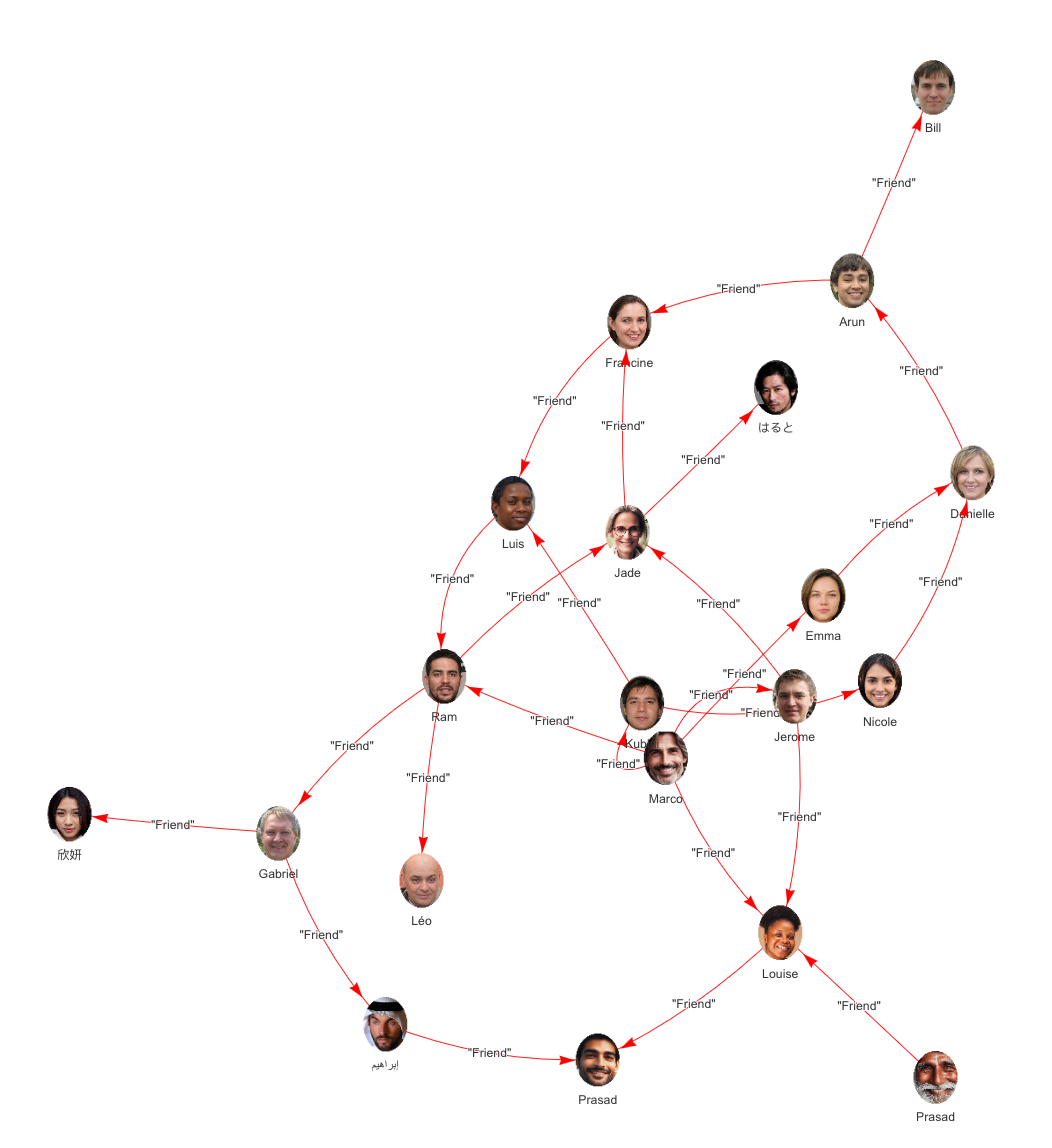
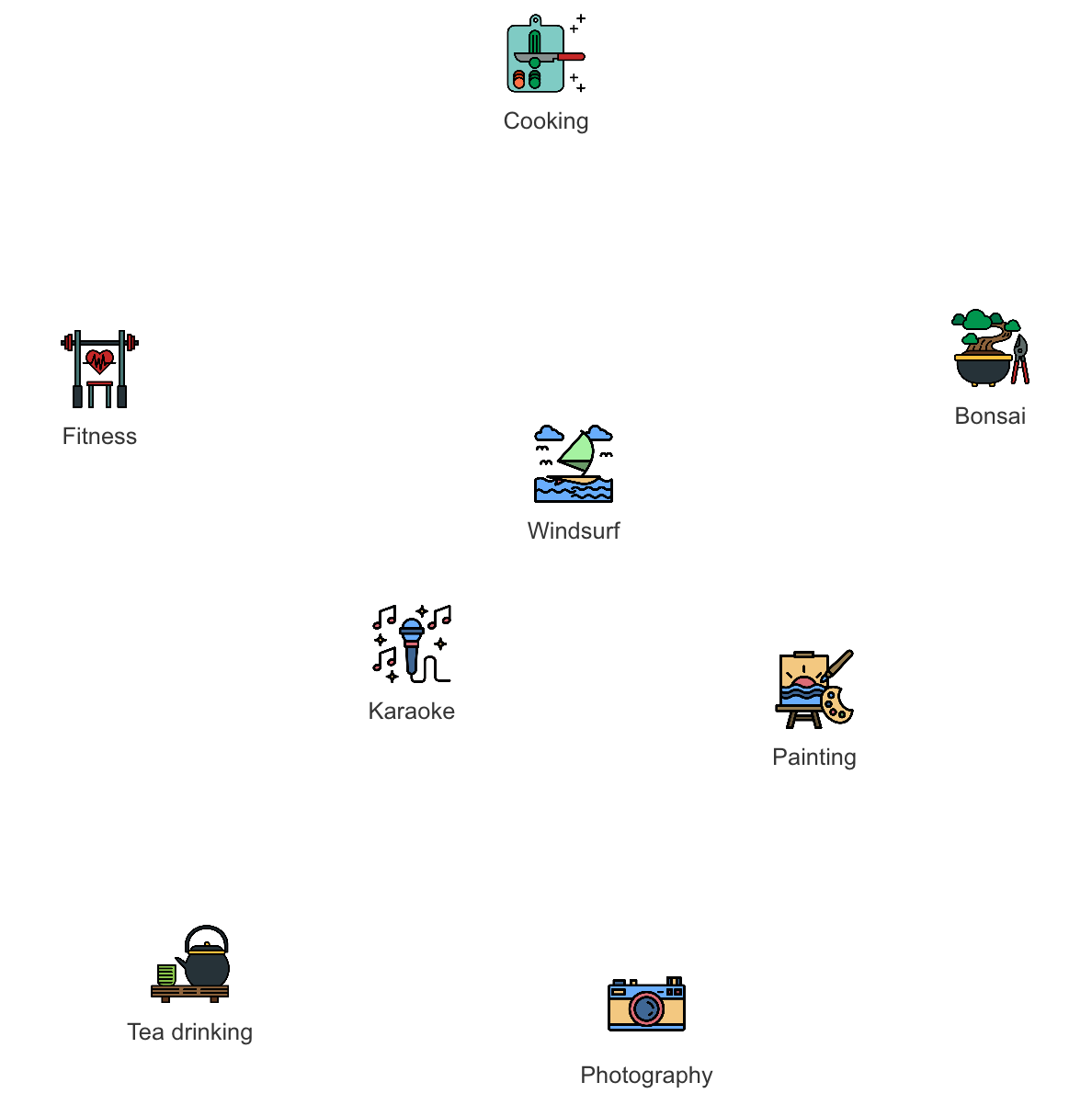
To help you visualize what's possible with FlexVertex and its SQL implementation, imagine you’re building a new app to identify prospective customers for a new travel promotion. You have data about people, their friends, their interests, and places they’ve visited. This small, sample collection of information is known as a constellation. Each script in this guide will utilize all or part of this constellation.
¶ Constellation data
This following small, sample collection of information is known as a constellation. Each script in this guide will evaluate all or part of the contents of this constellation.
¶ People

¶ Friends
¶ Interests
¶ Destinations

Whenever feasible, we keep the examples as small and focused as possible.
¶ Basic queries
For this section, we'll examine a collection of the simplest queries.
¶ SELECT all data
SELECT * FROM Destination
Retrieves all properties in all Destination objects.
SELECT Location, Type FROM Destination
Retrieves two properties in all Destination objects. Note that if you want to display results graphically and have appropriate assets be shown, be sure to include the ImageKey in the query:
SELECT Location, Type, ImageKey FROM Destination
¶ Sorting AND grouping
¶ Ascending sort
SELECT * FROM Person ORDER BY InfluencerRating
Retrieve all properties FROM all Person objects, sort by InfluencerRating
SELECT Name FROM Person ORDER BY InfluencerRating
Retrieve just the Name property FROM all Person objects, sort by InfluencerRating
¶ Descending sort
SELECT * FROM Person ORDER BY DOB DESC
Retrieve all properties FROM all Person objects, descending sort by DOB
SELECT Name, InfluencerRating FROM Person ORDER BY DOB DESC
Retrieve just the Name and InfluencerRating properties FROM all Person objects, descending sort by DOB
¶ Filtering
Filtering IN SQL is achieved using the WHERE clause, which allows users to specify conditions that the returned rows must meet. This mechanism helps in refining the query results by including only the data that matches the criteria specified in the WHERE clause. In this section, we examine a diverse collection of filtered queries.
¶ Simple WHERE filter
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Name='Marco'
Retrieves all properties in Person objects where the Name property equals 'Marco'.
¶ Multiple WHERE filters using OR
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Name='Marco' OR Name='Danielle'
Retrieves all properties from all Person objects where the Name property is either 'Marco' or 'Danielle'.
¶ Multiple WHERE filters using AND
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Name='Prasad' AND Age=25
Retrieves all properties from all Person objects where the Name property is 'Prasad' and the Age property is 25.
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Name='Prasad' AND (Age > 20 AND Age < 80)
Retrieves all properties from all Person objects where the Name property is 'Prasad' and the Age property is between 21 and 79.
¶ Multiple WHERE filters using AND combined with OR
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Name='Prasad' AND (Age > 30 OR InfluencerRating > 80)
Retrieves all properties FROM all Person objects where the Name property is 'Prasad' and the Age property is greater than 30 or the InfluencerRating is greater than 80.
¶ IN usage with integers
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Age IN (25, 26, 75, 76)
Retrieves all properties for Person objects where the Age property is in the list of provided VALUES.
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Age IN !(25, 26, 75, 76)
Retrieves all propertieds for all Person objects where the Age property is not in the list of provided values.
¶ IN usage with strings
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Name IN ('Marco', 'Nicole', 'Danielle', 'Kublai', 'إبراهيم')
Retrieves all properties in all Person objects where the Name property is in the list of provided values.
SELECT * FROM Person WHERE Name IN !('Marco', 'Nicole', 'Danielle', 'Kublai', 'إبراهيم')
Retrieves all properties in all Person objects where the Name property is not in the list of provided values.
¶ COUNT(*) function
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Interest
Returns a count of all Interest objects.
¶ COUNT function with property
SELECT COUNT(Age) FROM Person
Returns a count of all Person objects with a non-null Age property.
¶ LIMIT number of objects
SELECT * FROM Person LIMIT 5
Return all properties from no more than five Person objects.
¶ LIMIT return all objects
SELECT * FROM Person LIMIT -1
Return all properties from all Person objects.
¶ Creating data
¶ INSERT with VALUES
INSERT INTO Person (Name,DOB,InfluencerRating) VALUES ('Walter', DATE('1970-10-26'),25)
Create a new Person object using VALUES.
¶ INSERT with SET
INSERT INTO Person SET Name = 'Maude', DOB = DATE('1983-05-17'), InfluencerRating = 89
Create a new Person object using SET.
¶ Modifying data
¶ UPDATE using a filter
UPDATE Person SET InfluencerRating = 99 WHERE Name = 'Maude'
Update an existing Person object using a WHERE clause
¶ UPDATE AND create a new property
UPDATE Person SET NewProperty = 'New data'
Update all Person objects, creating a new property named NewProperty and setting a value for it
¶ UPDATE all objects
UPDATE Person SET NewProperty = 'Replaced data`
Update all the NewProperty properties for all Person objects
¶ Removing data
¶ DELETE using a filter
DELETE FROM Person WHERE Name = 'Walter'
Delete any Person objects using the Name property to filter